I. Understanding PNG Format
PNG, or Portable Network Graphics, is a widely used image file format known for its lossless compression and support for transparency. Introduced in the mid-1990s as a successor to the GIF format, PNG has become a popular choice for various applications due to its versatility and high-quality image reproduction.

Features and characteristics
PNG files are characterized by their ability to store high-quality images with minimal loss of detail. Unlike JPG, which uses lossy compression, PNG employs lossless compression techniques, preserving image quality while achieving smaller file sizes. Additionally, PNG supports alpha channel transparency, making it ideal for images with complex backgrounds or overlays.
Common uses
PNG files are commonly used for various purposes, including web graphics, digital photography, and graphic design. They are well-suited for images requiring transparent backgrounds, such as logos, icons, and illustrations. PNG’s ability to maintain image quality across multiple editing sessions makes it a preferred choice for professional graphic designers and photographers.
Advantages and disadvantages
The primary advantage of the PNG format is its ability to preserve image quality while supporting transparency, making it ideal for images with complex backgrounds or overlays. However, PNG files tend to be larger than formats like JPG, impacting storage and bandwidth requirements. Additionally, PNG may not be suitable for photographs or images with extensive gradients, as it may result in larger file sizes compared to JPG compression.
II. Understanding JPG Format
JPG, or Joint Photographic Experts Group, is a widely used image file format known for its efficient compression and widespread compatibility. Introduced in the early 1990s, JPG quickly became the standard format for digital photography and is widely supported by web browsers, image editing software, and digital cameras.
Features and characteristics
JPG files are characterized by their efficient compression algorithms, which significantly reduce file size while maintaining acceptable image quality. Unlike PNG, which uses lossless compression, JPG employs lossy compression techniques, sacrificing some image detail to achieve smaller file sizes. This makes JPG ideal for storing and sharing photographs and images online.

Common uses
JPG files are commonly used for various applications, including digital photography, web graphics, and social media. They are particularly well-suited for photographs and images with complex color gradients, as JPG compression allows for efficient storage and transmission of such images. Additionally, JPG’s widespread compatibility makes it a preferred choice for sharing images across different platforms and devices.
Advantages and disadvantages
The primary advantage of the JPG format is its efficient compression, which allows for a significant reduction in file size without significant loss of image quality. This makes JPG ideal for web-based applications with limited bandwidth and storage space. However, JPG compression is inherently lossy, meaning that repeated editing and saving of JPG files can result in a gradual degradation of image quality over time.
III. Reasons for Converting PNG to JPG
While PNG and JPG are both widely used image formats, there are several reasons why users may choose to convert PNG to JPG format. These reasons include reducing file size, improving compatibility with web and mobile platforms, and simplifying image storage and sharing processes.
File size reduction
One of the primary reasons for converting PNG to JPG format is to reduce file size. JPG compression typically results in smaller file sizes compared to PNG, making it more efficient for storing and sharing images online. This can be particularly beneficial for websites and applications with limited bandwidth and storage space.

Compatibility with web and mobile platforms
JPG is widely supported by web browsers, mobile devices, and image editing software, making it a preferred choice for images intended for online use. Converting PNG to JPG format ensures compatibility across different platforms and devices, allowing seamless sharing and displaying of images online.
Simplifying image storage and sharing
Converting PNG to JPG format can simplify image storage and sharing processes, especially when dealing with large volumes of images. JPG’s smaller file sizes make it easier to upload, download, and transmit images online, reducing the time and resources required for image management and distribution.
IV. Considerations and Best Practices
When converting PNG to JPG format, it is essential to consider various factors and adhere to best practices to ensure optimal results. These considerations include choosing between lossy and lossless compression, adjusting quality settings and compression ratios, and retaining important image details during conversion.
Lossy vs. lossless compression
Users must decide whether to use lossy or lossless compression when converting PNG to JPG format. Lossy compression results in smaller file sizes but may lead to some loss of image quality, especially in areas with fine details or gradients. In contrast, lossless compression preserves image quality but typically results in larger file sizes.
Quality settings and compression ratios
Adjusting quality settings and compression ratios is crucial for achieving the desired balance between file size and image quality. Higher compression ratios result in smaller file sizes but may lead to more noticeable loss of image detail. It is essential to experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance for each image.
Retaining important image details during conversion
When converting PNG to JPG format, retaining important image details, such as colors, textures, and shapes, is essential. This can be achieved by adjusting compression settings carefully and avoiding excessive compression that may result in loss of detail. Additionally, using image editing software to pre-process images before conversion can help optimize image quality.
V. Potential Challenges and Solutions
While converting PNG to JPG format offers many benefits, users may encounter challenges such as loss of image quality, handling of transparent backgrounds, and efficient processing of large batches of images. However, these challenges can be mitigated by implementing appropriate solutions and best practices.
Loss of image quality during conversion
One potential challenge when converting PNG to JPG format is the loss of image quality due to compression. To minimize this risk, users should carefully adjust compression settings and avoid excessive compression that may result in visible artifacts or loss of detail. Additionally, using image editing software to pre-process images before conversion can help optimize image quality.
Handling of transparent backgrounds in PNGs
Another challenge when converting PNG to JPG format is handling transparent backgrounds. Since JPG does not support transparency, transparent areas in PNG images will be filled with a solid color during conversion. To address this issue, users can manually remove transparent backgrounds or use image editing software to replace them with a solid color before conversion.
Dealing with large batches of images efficiently
Processing large batches of images efficiently can be challenging, especially when converting PNG to JPG format. To streamline the conversion process, users can use batch processing tools or scripts to automate repetitive tasks and optimize workflow efficiency. Additionally, leveraging cloud-based conversion services can help distribute processing load and speed up conversion times for large volumes of images.
VI. Impact on SEO and Website Performance
Choosing between PNG and JPG formats can significantly impact search engine optimization (SEO) and website performance. Image file size, format, and compression settings can influence page load times, user experience, and search engine rankings.
Effects of image file size on page load times
Large image file sizes can slow page load, leading to higher bounce rates and lower search engine rankings. By converting PNG to JPG format and optimizing compression settings, users can reduce image file sizes and improve website performance, resulting in faster page load times and better user engagement.
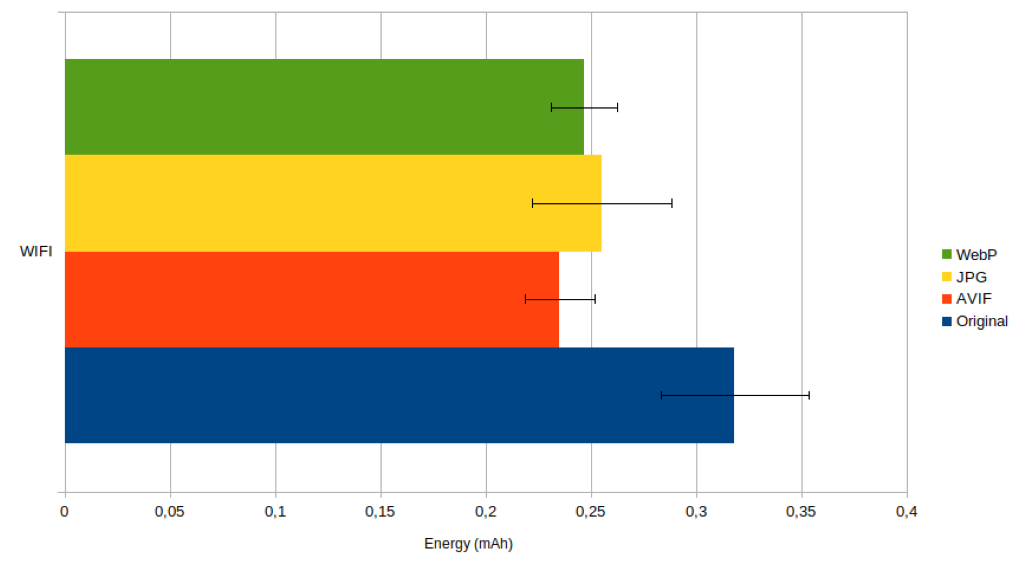
SEO implications of using JPGs over PNGs
Search engines consider various factors when ranking web pages, including page load times, user experience, and image optimization. Since JPG files typically have smaller file sizes than PNG, using JPGs over PNGs can improve website performance and SEO rankings. Optimizing image metadata, such as alt text and file names, can enhance image SEO.
Strategies for optimizing images for web performance
To optimize images for web performance, users should convert PNG to JPG format and adjust compression settings to achieve the optimal balance between file size and image quality. Additionally, resizing images to the appropriate dimensions and using responsive image techniques can improve website performance across different devices and screen sizes.
VII. Future Trends and Developments
As technology continues to evolve, the landscape of image conversion is poised for significant advancements and innovations. Emerging trends in image compression technology, the emergence of new image formats, and the integration of AI in image conversion processes are shaping the future of image format optimization.
Advances in image compression technology
Advancements in image compression technology drive innovation in image format optimization, with algorithms capable of achieving higher compression levels without significant loss of image quality. Future developments include more efficient compression techniques, improved support for emerging image formats, and enhanced integration with web and mobile platforms.
Emergence of new image formats
The emergence of new image formats is expanding the possibilities for image format optimization, with formats like WebP and AVIF offering superior compression efficiency and image quality compared to traditional formats like JPG and PNG. As these new formats are adopted, users may have more options for optimizing images for web and mobile platforms.
Integration of AI in image conversion processes
Integrating AI and machine learning in image conversion processes revolutionizes how images are compressed, optimized, and converted between different formats. AI-powered algorithms can analyze image content, predict perceptual image quality, and optimize compression settings to achieve the best possible results. This technology has the potential to automate and streamline the image conversion process, making it faster, more efficient, and more accessible to users.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, converting PNG to JPG format offers many benefits, including reduced file sizes, improved compatibility with web and mobile platforms, and simplified image storage and sharing processes. By understanding the considerations and best practices involved in image format conversion, users can achieve optimal results while preserving image quality and maximizing website performance. As technology continues to evolve, future advancements in image compression technology, the emergence of new image formats, and the integration of AI in image conversion processes will shape the future of image format optimization.
Recap of the significance of PNG to JPG conversion
Converting PNG files to JPG format is essential for optimizing image file sizes, improving compatibility with web and mobile platforms, and enhancing website performance and SEO rankings. By leveraging best practices and emerging technologies, users can achieve optimal results and stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly evolving landscape of image format optimization.
Recommendations for effective implementation
To ensure effective implementation of PNG to JPG conversion, users should carefully consider factors such as compression settings, image quality, and compatibility requirements. Additionally, staying informed about emerging trends and developments in image compression technology can help users make informed decisions and stay ahead of the curve.
Future directions for image format optimization
The future of image format optimization is bright, with advancements in compression technology, the emergence of new image formats, and the integration of AI in image conversion processes driving innovation and shaping the way images are stored, shared, and displayed online. By embracing these trends and developments, users can unlock new opportunities for optimizing image formats and enhancing the digital imaging experience.
IX. FAQs
What are the main differences between PNG and JPG formats?
PNG is a lossless image format supporting transparency, while JPG is a lossy image format offering efficient compression but not transparency.
How does image format conversion impact website performance?
Converting PNG to JPG format can reduce image file sizes, leading to faster page load times and improved website performance, positively impacting user experience and search engine rankings.
Are there any drawbacks to converting PNG files to JPG format?
Converting PNG to JPG format may result in some loss of image quality due to compression. Additionally, JPG does not support transparency, so transparent areas in PNG images will be filled with a solid color during conversion.
What is the best way to optimize images for web performance?
To optimize images for web performance, users should convert PNG to JPG format, adjust compression settings to achieve the optimal balance between file size and image quality, and resize images to the appropriate dimensions for display on different devices and screen sizes. Optimizing image metadata and using responsive image techniques can enhance website performance.
